
Leading Oil and Gas Companies in Saudi Arabia: Growth and Outlook
Introduction: Saudi Arabia’s Petrochemical Industry in Global Markets
Saudi Arabia’s petrochemical industry is important in both the national and international energy markets. The country uses its plenty of oil and gas resources, and oil and gas companies in Saudi Arabia benefit from good infrastructure and advanced refining and chemical making to become the world’s biggest exporter of petrochemical products. Therefore, the petrochemical industry in Saudi Arabia helps international markets with important chemicals and plastics, and also supports economic growth and efforts to make energy more sustainable, as part of Saudi Vision 2030.

Key Statistics of the Saudi Petrochemical Sector
How significant is Saudi Arabia’s share in the global petrochemical market? Saudi Arabia petrochemical industry is a major player in oil, gas, and petrochemicals. Here are some key facts that show the size and influence of the Saudi petrochemical sector:
-
Population: 36+ million
-
Area: 2.2 million km²
-
GDP: $1.238 trillion
-
Proven Oil Reserves: 267 billion barrels
-
Crude Oil Production: 9 million barrels/day
-
Crude Oil Exports: ~8 million barrels/day
-
Major Oil Fields: Ghawar Oil Field Saudi Arabia (the largest), Safaniya, Khurais, Shaybah, Qatif
-
Proven Gas Reserves: 229 TCF
-
Natural Gas Production: 11 BCF/day
-
Major Companies: Aramco, SABIC, YANSAB, GPIC
-
Petrochemical Exports: $50 billion
-
Contribution to GDP: 35–40%
These oil fields in Saudi Arabia represent some of the largest proven reserves worldwide ,and how important it is to both the local economy and global supply chains.

Major Companies Driving Saudi Arabia’s Petrochemical Industry
Saudi Arabia’s petrochemical industry is driven by top oil and gas companies in Saudi Arabia, that help both local growth and international markets. Some of the main companies are:
Saudi Aramco
- Founded in 1933, based in Dhahran
- Handles the exploration, development, and production of oil and gas
- Runs major fields like Ghawar and Safaniya
- Works in refining, chemical production, and renewable energy
Saudi Basic Industries Corporation (SABIC)
- Started in 1976, fully owned by the government
- Operates globally in chemicals, polymers, mining, and refining
- Works closely with Aramco to strengthen the Saudi petrochemical industry
Yanbu Petrochemical Industries Company (YANSAB)
- Joint venture with Shell
- Manages chemical industrial parks around Yanbu
- Focuses on chemical and polymer production
Gulf Petrochemical Industries Company (GPIC)
- Based in Manama, Bahrain
- Jointly owned by Saudi Arabia and regional investors
- Contributes to petrochemical exports and industrial development
Together, these companies are the foundation of the Saudi petrochemical sector and help keep the country leading in energy and chemicals.
Chemical Industrial Parks in Saudi Arabia
Which industrial zones offer the best chances for chemical park projects? Saudi Arabia is developing special chemical industrial parks that support its major companies and help the country stay competitive globally. These zones are near resources, export routes, and trade networks, creating places where refining, petrochemicals, and advanced manufacturing can happen together.
-
Dammam Industrial City Dammam Industrial City is one of Saudi Arabia’s oldest and most developed industrial areas. It is near King Abdulaziz Port and major roads. It supports many industries, including chemicals and manufacturing. It has good logistics, utilities, and is conveniently located near both local and international markets. This helps the Saudi Arabia petrochemical industry.
-
Jubail Industrial City Jubail Industrial City is the world’s largest petrochemical hub. It is home to top global and regional chemical producers. It has top-notch infrastructure, deep-water ports, and integrated utility systems. It supports large-scale projects in downstream and specialty chemicals, helping the Saudi petrochemical sector.
-
King Abdullah Economic City King Abdullah Economic City has zones for industry, logistics, and living. Located on the Red Sea coast, it offers direct access to global markets via King Abdullah Port. The city features solid infrastructure, straightforward rules, and available land for various industries, including chemicals and petrochemicals.
-
Ras Al-Khair Special Economic Zone Ras Al-Khair is a specialized area focused on heavy industries, chemicals, and maritime activities. It features top facilities for refining, mineral processing, and chemical manufacturing. Its strategic location and government backing make it an ideal site for export projects that support the Saudi petrochemical sector.
-
Yanbu Industrial City Yanbu Industrial City is a major petrochemical and refining hub on the Red Sea coast. It is an important gateway for Saudi energy and chemical exports. It has modern ports, pipelines, and utilities. Yanbu continues to attract global chemical investments, helping the sector diversify and grow.
These industrial zones not only drive domestic economic diversification but also serve as global export centers, reinforcing Saudi Arabia’s leadership in energy, chemicals, and sustainable industrial development.
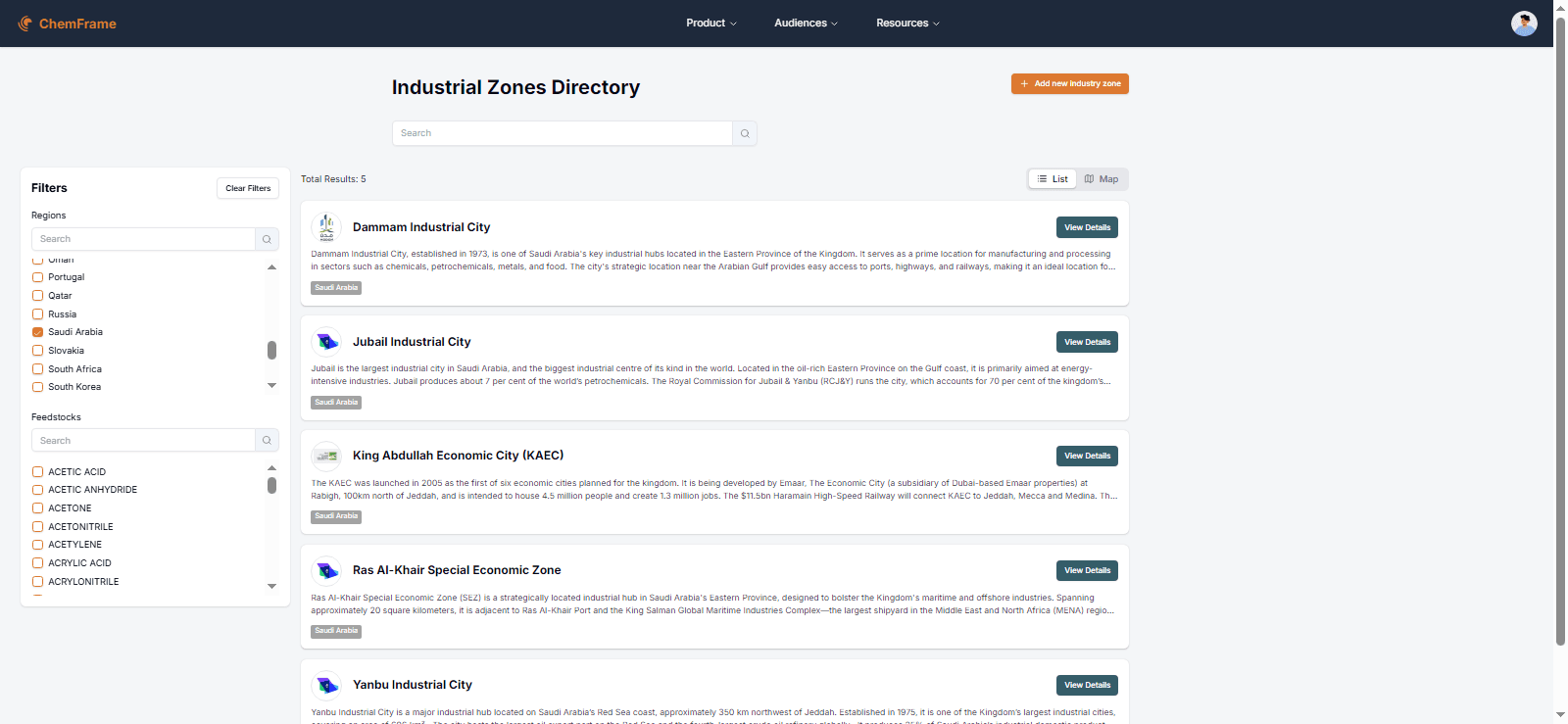
Chemframe’s Industrial Zones directory provides a full overview of Saudi Arabia’s chemical and chemical industrial parks, detailing infrastructure, feedstocks, utilities, and contacts. Our platform enables investors, licensors, and project developers to explore opportunities and engage with key industry players.

Strengths and Advantages of the Saudi Petrochemical Industry
Saudi Arabia’s petrochemical industry has several strong points that help it lead globally. Oil and gas companies in Saudi Arabia leverage abundant and low-cost feedstock to maintain a competitive edge. Saudi Arabia’s petrochemical industry has several strong points that help it lead globally:
- Access to cheap feedstock Abundant and low-cost oil and gas reserves give the country a strong competitive advantage in petrochemical production.
- Strong export infrastructure Extensive ports, pipelines, and logistics networks allow efficient delivery of crude oil, gas, and petrochemical products to international markets.
- Strategic geographic location Located at the heart of the Middle East, Saudi Arabia provides easy access to major export markets in Asia, Europe, and beyond, making the Saudi petrochemical industry highly competitive for oil and gas companies in Saudi Arabia.
Challenges Facing Saudi Arabia’s Petrochemical Sector
Challenges Facing Saudi Arabia’s Petrochemical Sector What challenges does the Saudi petrochemical industry face, and how can investors mitigate risks? Despite being a global leader, the Saudi petrochemical industry faces several important challenges:
- Environmental pressure – Increasing global demand for low-carbon and sustainable chemicals, stricter emission standards, and initiatives like blue/green hydrogen and carbon capture require ongoing investment in clean technologies.
- Feedstock dependency – The industry relies heavily on oil and gas as primary raw materials, which affects oil and gas companies in Saudi Arabia. Volatility in crude oil prices from oil fields in Saudi Arabia can significantly impact production costs and competitiveness.
- Infrastructure gaps in gas distribution – While eastern regions have extensive pipelines, western and southern areas lack sufficient capacity, which can limit industrial growth and energy efficiency.
- Increasing global competition – New petrochemical hubs in Asia, the Middle East, and the Americas intensify competition, putting pressure on Saudi producers to innovate, diversify products, and maintain market share.
- Transition to higher-value products – Moving from basic commodity chemicals to specialty and downstream products requires technological upgrades, workforce training, and strategic investments aligned with Saudi Vision 2030.
Recent Investments and Developments in Saudi Petrochemicals
Recent Investments and Developments in Saudi Petrochemicals Saudi Arabia continues to expand its petrochemical and energy sectors with strategic investments in advanced technologies and sustainable production:
-
Aramco & TotalEnergies – Amiral Petrochemical Complex A $11 billion facility, set to begin operations in 2027, will produce ethylene, polymers, MTBE, and specialty chemicals, strengthening Saudi Arabia as a hub for advanced petrochemicals and clean energy.
-
Blue & Green Hydrogen Projects Aramco and NEOM are developing large-scale blue and green hydrogen and low-carbon ammonia projects for export to Asia and Europe, supporting sustainability goals under Saudi Vision 2030 and the Saudi petrochemical industry.
-
SABIC CO₂ Capture and Purification Facility SABIC operates the world’s largest CO₂ capture facility, integrating carbon reduction technologies into petrochemical production and advancing sustainable industry practices.
Future Outlook: Saudi Petrochemical Industry under Vision 2030
Saudi Arabia petrochemical industry is expected to grow steadily over the coming years, driven by strategic diversification, investments in higher-value downstream products, and rising global demand for plastics, fertilizers, and specialty chemicals. Initiatives in clean energy, blue and green hydrogen, and sustainable production technologies are set to further strengthen the country’s position as a global leader in the petrochemical sector. With resources like the Ghawar Oil Field Saudi Arabia, the country continues to lead in energy and petrochemicals.
Frequently Asked Questions About Oil and Gas Companies in Saudi Arabia
1. What makes Saudi Arabia’s petrochemical industry important globally?
Saudi Arabia is the world’s largest exporter of petrochemical products, leveraging abundant oil and gas resources, advanced infrastructure, and integrated refining and chemical production to supply essential chemicals and polymers to international markets.
2. Which are the major oil fields in Saudi Arabia?
The Ghawar Oil Field Saudi Arabia (largest onshore) and Safaniya offshore field are the country’s key oil fields, forming the backbone of its crude oil and petrochemical production.
3. Who are the leading petrochemical companies in Saudi Arabia?
Major players include Saudi Aramco, SABIC, Yanbu Petrochemical Industries Company (YANSAB), and Gulf Petrochemical Industries Company (GPIC). They oversee exploration, refining, chemical production, and exports.
4. What are Saudi Arabia’s main strengths in petrochemicals?
Key strengths include access to cheap feedstock, strong export infrastructure, and a strategic geographic location, allowing efficient production and delivery to global markets.
5. What challenges does the Saudi petrochemical industry face?
Challenges include environmental pressures, dependency on oil and gas feedstock, infrastructure gaps in gas distribution, rising global competition, and the transition to higher-value products under Saudi Vision 2030.
6. How much crude oil does Saudi Arabia produce and export?
In 2024, Saudi Arabia produces around 9 million barrels of crude oil per day, exporting approximately 8 million barrels daily, making it the world’s largest crude oil exporter.
7. What recent investments are shaping the industry?
Notable developments include the Amiral Petrochemical Complex ($11 billion, opening in 2027), blue and green hydrogen projects with Aramco and NEOM, and SABIC’s CO₂ capture facility, advancing sustainability and downstream production.
8. How is natural gas used in Saudi Arabia?
Saudi Arabia produces 11 BCF/day of natural gas, primarily for electricity generation, water desalination, and feedstock for petrochemical plants, with about 80% used by the industrial sector.
9. How does the petrochemical sector contribute to the economy?
Petrochemical exports reached $50 billion in 2021, contributing 35–40% of Saudi Arabia’s GDP and employing a significant portion of the workforce while supporting diversification under Vision 2030.
10. What is the future outlook for Saudi Arabia’s petrochemical industry?
The industry is expected to grow steadily, driven by diversification into higher-value downstream products, global demand for plastics and fertilizers, and initiatives in clean energy, blue/green hydrogen, and sustainable technologies.